Cocoa Impact Report – 2021

Our Geographic Reach
Global cocoa production has grown to over 4 million tons a year and is dominated by Côte d’Ivoire, which produces around 2.2 million tons annually, and Ghana (1.1 million tons in 2021). Together, these two countries account for over 50% of the world’s cocoa output. The global Fairtrade cultivation area of organic cocoa increased by 3% in 2020. Côte d’Ivoire, Ghana, and the Dominican Republic remained the top 3 largest producers of Fairtrade cocoa for the United States.

Cóte d'Ivoire

The Dominican Republic

Ghana


Our Collective Impact
Living Incomes can be truly transformational for families and their communities. It offers the opportunity to achieve sustainable yields and improve farm efficiency, and ensure farmers are paid sustainable price for their crop. Fairtrade defines a living income as enough to afford decent housing, food, clothing, education, healthcare, and other essential household expenses. For cocoa farmers, earnings usually come from farming activities as well as from off-farm work. Fairtrade’s holistic living income model addresses multiple factors of farmer success: sustainable farm yield, viable farm size, and a commodity price that supports the costs of sustainable production, including payment of a living wage to hired workers. Based on data collected from farm records, we have set Fairtrade Living Income Reference Prices for cocoa from Côte d’Ivoire and Ghana since 2018. These are voluntary prices that companies can pay to Fairtrade cooperatives they source from to enable living incomes in their supply chains.
The Fairtrade Cocoa Market Landscape in the US
According to consumer research conducted in partnership with GlobeScan, in 2021 53% of consumers used their buying power to make a positive difference on an issue they care about. Many chose to put more Fairtrade items into their shopping carts. NCA’s third annual State of Treating report reveals that the total US confectionery category hit $36.9 billion in retail sales in 2021. US Fairtrade cocoa sales volumes grew by 11%.
73% of Fairtrade shoppers were willing to pay more for a product to ensure farmers and workers were paid a fair price; specifically, up to 30% more for a bar of chocolate.
80% of consumers would feel more positively about a brand if it started carrying the Fairtrade Mark
9/10 of customers are interested in learning about a confectionery brand’s environmental commitments and social responsibility practices on the package label, the brand’s website, or social media.
US Sales, Volumes & Premiums
New business commitments complement long-standing partnerships that drive significant impact for cocoa farmers. Fairtrade’s partnership with the corporate sector has generated around $3.2 million in Premium, supporting almost 440,000 cocoa farmers to invest in their organizations and increase their earnings in 2021. The volume of sales represented 16 million pounds, an 11% increase over the previous year.
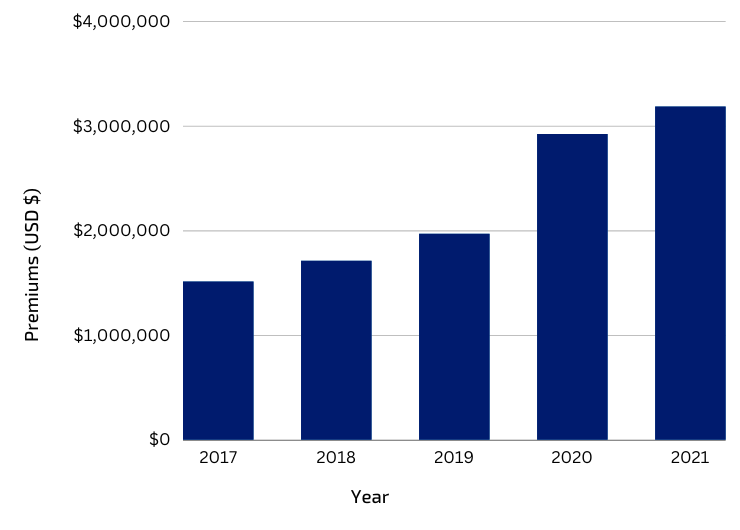
Cocoa Premiums Generated through Fairtrade Sales, 2017-2021
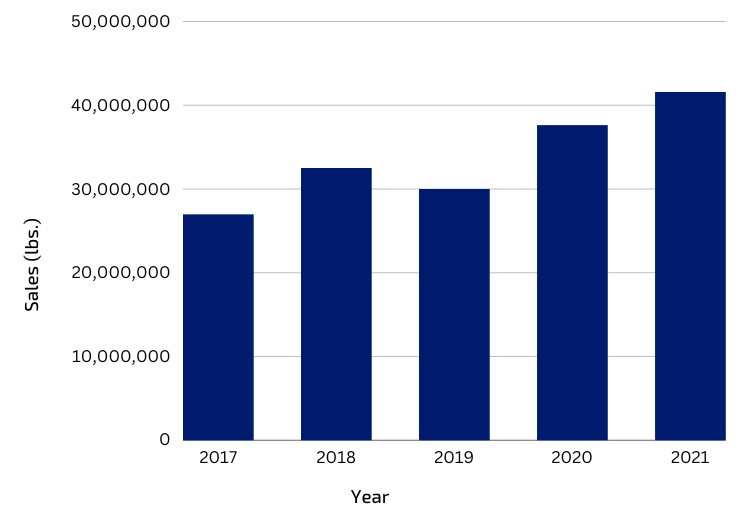
Fairtrade Cocoa Sales Volume (lbs), 2017-2021
The Fairtrade Premium
The Fairtrade Premium is the hallmark of Fairtrade America’s certification model. On top of the price that farmers and workers receive for their commodity or labor, they receive an extra sum of money to invest in improving the quality of their lives. The Fairtrade Premium is calculated as a percentage of the volume of products sold. The price is reviewed every two to three years to adjust to local inflation.
As part of the Fairtrade International network, farmers join with other farmers in local cooperatives. The Fairtrade Premium is paid at the cooperative level, so Fairtrade farmers’ democratically elected representatives vote on how the money is used to support business and community development. We believe that farmers are in a much better position to decide what investments will improve the quality of their lives and know best how to spend this money.
Producer Highlight: CONACADO
 The Dominican Republic is the second lowest income country in the Caribbean after Haiti, with 40% of its population living below the poverty line. Cocoa is grown there by around 40,000 small-scale cocoa growers.
The Dominican Republic is the second lowest income country in the Caribbean after Haiti, with 40% of its population living below the poverty line. Cocoa is grown there by around 40,000 small-scale cocoa growers.
CONACADO cocoa cooperative in Santo Domingo is made up of 182 small-scale producer associations with a total membership of 10,000 cocoa farmers. The average farm is 4.3 hectares (10.6 acres) where cocoa is grown under the shade canopy of tall native trees and smaller banana, citrus, and avocado trees whose fruit is sold at the local market. Vegetables are also grown for home consumption.
Almost half of CONACADO’s members’ products are now sold on Fairtrade terms, and the additional income received through Fairtrade Premiums has been invested in processing and warehouse facilities to improve the quality of their cocoa. Last year, 30 extension officers were employed to provide technical training to support farmers in improving yields, converting to organic production, and planting new trees. Schools have been built and repaired, with scholarships and equipment provided to students from lower income families. A new IT center helps children with schoolwork and brings the internet to the community. A clinic, free medical checks, and clean water projects are improving community health.
Benefits of Fairtrade, according to Farmers
From 2016 to 2018, we collected data from eight cocoa producer organizations to better understand how producers are gaining power in trade relationships and building sustainable livelihoods through Fairtrade.

90% of Fairtrade cocoa farmers reported Fairtrade remains an important source of livelihood

93% of Fairtrade cocoa farmers reported that the Fairtrade Premium stands out as a key benefit of Fairtrade

91% of Fairtrade cocoa farmers reported they received high levels of services and training through producer network support
Fairtrade Premium Use by SDGs
The Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) are an ambitious set of 17 overarching global goals adopted by the UN General Assembly in 2015 to combat poverty and achieve sustainable development. The goals set the ambition of ending poverty “in all its forms, everywhere,” while leaving no one behind. They represent a powerful opportunity to improve the lives of the 1.3 billion small-scale farmers and agricultural workers upon whom the world depends to produce our food and protect our planet.
But what does this look like on the ground? And how is Fairtrade playing a part in meeting the new goals?
Fairtrade Premium investments made by cocoa producers contribute to several of the SDGs. While most activities can apply to more than one SDG, here we have mapped each category of spending to a unique SDG for simplicity:
![]() SDG1 (no poverty) aims to end poverty in all its forms everywhere. This goal is central to Fairtrade’s mission. Twenty-three percent of the Fairtrade Premium was allocated towards credit services and direct payments to farmer members. Supplemental programs have been introduced so that farmers and workers progress towards a living income and living wages.
SDG1 (no poverty) aims to end poverty in all its forms everywhere. This goal is central to Fairtrade’s mission. Twenty-three percent of the Fairtrade Premium was allocated towards credit services and direct payments to farmer members. Supplemental programs have been introduced so that farmers and workers progress towards a living income and living wages.
![]() SDG2 (zero hunger) aims to end hunger, achieve food security and improve nutrition, and promote sustainable agriculture. Fifty-eight percent of the Fairtrade Premium was reinvested back into farmer organizations, strengthening their ability to participate in markets, access affordable credit, and invest in infrastructure.
SDG2 (zero hunger) aims to end hunger, achieve food security and improve nutrition, and promote sustainable agriculture. Fifty-eight percent of the Fairtrade Premium was reinvested back into farmer organizations, strengthening their ability to participate in markets, access affordable credit, and invest in infrastructure.
![]() SDG11 (sustainable cities & communities) aims to make cities and human settlements inclusive, safe, resilient, and sustainable: Producer organizations are pillars in their communities and are reported to have allocated 9% of their Fairtrade Premium toward social and economic services for communities, including sustainable transportation, the construction of warehouses, bridges, and resilient infrastructure.
SDG11 (sustainable cities & communities) aims to make cities and human settlements inclusive, safe, resilient, and sustainable: Producer organizations are pillars in their communities and are reported to have allocated 9% of their Fairtrade Premium toward social and economic services for communities, including sustainable transportation, the construction of warehouses, bridges, and resilient infrastructure.
Beyond Certification: Fairtrade Producer Projects
Fairtrade develops innovative, impact-oriented projects, funded by donors and partners with governments, NGOs, and the private sector to develop projects in line with our mission to empower producers and promote fairer trading conditions. These projects are producer-led and time-limited. The Alliances for Sankofa project, which aims to improve incomes, restore nature, and tackle climate change in cocoa, is just one example.
Alliances for Sankofa
The Sankofa project supports climate-smart farming practices in Ghana and promotes more resilient cocoa production and trade by training Kuapa Kokoo farmers to implement dynamic agroforestry (DAF) systems that improve food security and incomes through crop diversification and reforestation. The DAF system works primarily to improve the soil and biodiversity using various techniques: mulching, stratification, and planting a wide variety of trees and associated crops, including ones that are pruned each year and used for biomass.
Farmers are encouraged to stop burning organic matter, avoid using chemicals and promote biodiversity by planting a variety of trees and food crops to improve soil health and inset CO2 emissions. Carbon sequestration through these actions means farmers will earn and trade carbon credits from the trees in the future.
The project currently takes place on more than 400 hectares and directly benefits the 2,900 members of the Kuapa Kokoo and their local community.
“Cocoa farming is very important so that I can take care of my children and grandchildren. Cocoa does very well under this system. I can earn money from selling the crops I grow, and I have food to feed my family.” – Emelia Debra, Cocoa Farmer
Celebrate and Grow Your Impact By:

Join private companies
We complement our certification services with a range of tailored programs, collaborating with farmers and workers to tackle issues impacting their communities. Join a range of private companies, governments, and civil society organizations, who have committed to funding Fairtrade projects to deliver maximum impact for farmers and workers across the world.

Show the impact
Showing the impact that you make through your Fairtrade certification lets customers know they should be proud to choose your Fairtrade products. We can provide marketing materials to help you show impact and tell your Fairtrade story.

Campaign with us
Our global community is leading the way towards a more ethical and sustainable world. Join us in demanding a fairer deal for the farmers and workers by amplifying the people and the causes you care about through our campaign advocacy.











